| CAS
NO. |
607-81-8 |
|
| EINECS NO. |
210-142-7 |
| FORMULA |
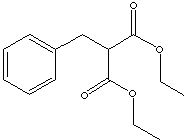
C6H5CH2CH(COOC2H5)2 |
| MOL
WT. |
250.29 |
|
H.S.
CODE
|
2917.39 |
|
SMILES |
|
|
TOXICITY
|
|
| SYNONYMS |
Diethyl-2-benzylmalonate;
|
| Benzylmalonic acid diethyl ester; Benzyl-Malonic acid, diethyl ester; Malonic acid, 2-benzyl-, diethyl ester; Benzylpropanedioic acid diethyl ester;
|
|
CLASSIFICATION
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
clear
to pale yellow liquid
|
| MELTING POINT |
|
| BOILING
POINT |
296 - 298 C |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
1.06
- 1.07
|
| SOLUBILITY
IN WATER |
Insoluble |
| pH |
|
| VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
|
NFPA
RATINGS
|
Health: 1; Flammability: 1; Reactivity: 0 |
|
AUTOIGNITION
|
1.4868 |
|
FLASH
POINT
|
>
110 C
|
| STABILITY |
Stable
under ordinary conditions. Moisture sensitive. |
|
GENERAL
DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS
|
|
Malonic acid (also called Propanedioic Acid ) is a white crystalline C-3
dicarboxylic acid; melting at 135 -136 C; readily soluble in water, alcohol and
ether; solution in water is medium-strong acidic. It can be derived by oxidizing
malic acid or by the hydrolysis of cyanacetic acid. Malonic acid itself is
rather unstable and has few applications. It's diethyl ester (diethyl malonate)
is more important commercially. Diethyl malonate, a colourless, fragrant liquid
boiling at 199 C, is prepared by the reaction of monochloroacetatic acid with
methanol, carbon monoxide or by the reaction cyanoacetic acid (the half
nitriled-malonic acid) with ethyl alcohol. Malonic acid and its esters contain
active methylene groups which have relatively acidic alpha-protons due to H
atoms adjacent to two carbonyl groups. The reactivity of its methylene group
provide the sequence of reactions of alkylation, hydrolysis of the esters and
decarboxylation resulting in substituted ketones. The methylene groups in
1,3-dicarboxylic acid utilize the synthesis of barbiturates; a hydrogen atom is
removed by sodium ethoxide, and the derivative reacts with an alkyl halide to
form a diethyl alkylmalonate. The diethyl dialkylmalonates are converted to
barbiturates by reaction with urea. Malonic acid and its esters are
characterized by the large number of condensation products. They are important
intermediates in syntheses of vitamins B1 and B6, barbiturates, non-steroidal
anti-inflammatory agents, other numerous pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals
and flavors & fragrances compounds. |
| SALES
SPECIFICATION |
|
APPEARANCE
|
clear
to pale yellow liquid
|
|
ASSAY
|
98.0%
in
|
|
ACID
VALUE
|
1
max (mg KOH/g) |
|
MOISTURE
|
0.1%
max |
| TRANSPORTATION |
| PACKING |
200kgs
in Drum |
| HAZARD CLASS |
Not
regulated |
| UN
NO. |
|
| OTHER
INFORMATION |
|
Hazard Symbols: n/a,
Risk Phrases: 36/38, Safety Phrases: 26-36 |
